引:算法一直很重要,最近没有心情去看项目的代码与技术,所以就拿起其了算法导论来看,最经典的快速排序及随机化算法,java实现。
快速排序算法
- 核心思想
分治思想和原址运算:看一张图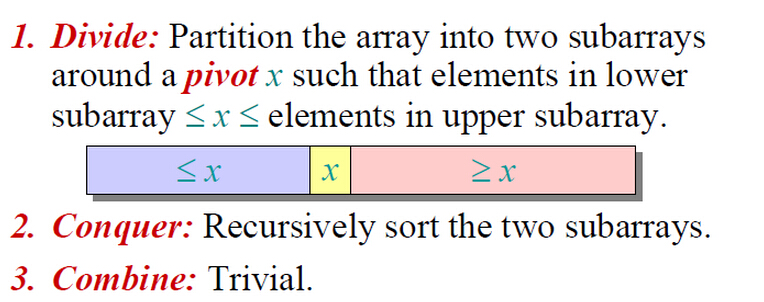
算法具体实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97public class QuickSort {
public int partition(int[] a,int p,int r){
int x = a[r];
int i = -1;
int temp = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < a.length-1; j++) {
if(a[j]<x){
i=i+1;
temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = temp;
}
}
temp = a[i+1];
a[i+1] = x;
a[r] = temp;
return i+1;
}
public int[] quicksort(int[] b,int p,int r){
if(p<r){
int q = partition(b,p,r);
quicksort(b, p, q-1);
quicksort(b, q+1, r);
}
return b;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
QuickSort sort = new QuickSort();
int[] a = {2,8,7,1,3,5,6,4};
int[] b = sort.quicksort(a, 0, a.length-1);
for (int i : b) {
System.out.print(i+" ");
}
}
}
3.时间复杂度
通过分析我们最看重的平均复杂度是nlgn
## 随机化算法
1. 核心思想
在算法加入随机性,要么在使序列生成随机化,要么就是使主元随机化,这里我们使主元随机化。
2. 算法具体实现
```java
import java.util.Random;
public class RandomQuickSort {
public int partition(int[] a,int p,int r){
int x = a[r];
int i = -1;
int temp = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < a.length-1; j++) {
if(a[j]<x){
i=i+1;
temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = temp;
}
}
temp = a[i+1];
a[i+1] = x;
a[r] = temp;
return i+1;
}
public int randompartition(int[] a,int p,int r){
int temp = 0;
Random random = new Random();
int i = random.nextInt(r);
temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[r];
a[r] = temp;
return partition(a, p, r);
}
public int[] randomquicksort(int[] b,int p,int r){
if(p<r){
int q = randompartition(b, p, r);
randomquicksort(b, p, q-1);
randomquicksort(b, q+1, r);
}
return b;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
RandomQuickSort sort = new RandomQuickSort();
int[] a = {2,8,7,1,3,5,6,4};
int[] b = sort.randomquicksort(a, 0, a.length-1);
for (int i : b) {
System.out.print(i+" ");
}
}
}时间复杂度
通过分析我们最看重的平均复杂度是nlgn
基本排序算法

小结:同等情况下快速排序>随机化算法>归并排序>插入排序;
在有序的情况下随机化算法>快速排序
总结
慢慢走,不要急!